216 lines
5.6 KiB
Markdown
216 lines
5.6 KiB
Markdown
|
|
# 毎日一题 - 417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
## 信息卡片
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* 时间:2019-08-13
|
|||
|
|
* 题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow
|
|||
|
|
- tag:`Backtracking` `DFS`
|
|||
|
|
## 题目描述
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
给定一个 m x n 的非负整数矩阵来表示一片大陆上各个单元格的高度。“太平洋”处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而“大西洋”处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
规定水流只能按照上、下、左、右四个方向流动,且只能从高到低或者在同等高度上流动。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
请找出那些水流既可以流动到“太平洋”,又能流动到“大西洋”的陆地单元的坐标。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
提示:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
输出坐标的顺序不重要
|
|||
|
|
m 和 n 都小于150
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
示例:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
给定下面的 5x5 矩阵:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
太平洋 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
|
|||
|
|
~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *
|
|||
|
|
~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *
|
|||
|
|
~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 *
|
|||
|
|
~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *
|
|||
|
|
~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *
|
|||
|
|
* * * * * 大西洋
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
返回:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[[0, 4], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 2], [3, 0], [3, 1], [4, 0]] (上图中带括号的单元).
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
## 参考答案
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 方法1:直接采用回溯法 超时
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
直接判断 水流既可以流动到“太平洋”,又能流动到“大西洋”的陆地单元的坐标
|
|||
|
|
采用方法是
|
|||
|
|
回溯法(英语:backtracking)是暴力搜索法中的一种。
|
|||
|
|
在最坏的情况下,回溯法会导致一次复杂度为指数时间的计算。
|
|||
|
|
在这个题目中,这个题目中正好就是如此。
|
|||
|
|
因为需要等到上下左右全部计算完毕才有确定答案。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
m 和 n =150,肯定超时。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 方法2:动态规划+回溯法
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
思路:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
总体思路还是回溯,我们对能够流入太平洋的(第一行和第一列)开始进行上下左右探测。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
同样我们对能够流入大西洋的(最后一行和最后一列)开始进行上下左右探测。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
最后将探测结果进行合并即可。合并的条件就是当前单元既能流入太平洋又能流入大西洋。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
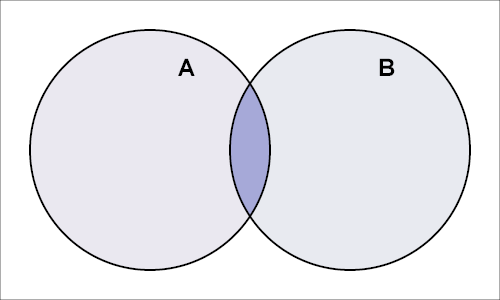
|
|||
|
|
扩展:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
如果题目改为能够流入大西洋或者太平洋,我们只需要最后合并的时候,条件改为求或即可
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
## 参考代码
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- JavaScript Code
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```js
|
|||
|
|
function dfs(i, j, height, m, matrix, rows, cols) {
|
|||
|
|
if (i >= rows || i < 0) return;
|
|||
|
|
if (j >= cols || j < 0) return;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
if (matrix[i][j] < height) return;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
if (m[i][j] === true) return;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
m[i][j] = true;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
dfs(i + 1, j, matrix[i][j], m, matrix, rows, cols);
|
|||
|
|
dfs(i - 1, j, matrix[i][j], m, matrix, rows, cols);
|
|||
|
|
dfs(i, j + 1, matrix[i][j], m, matrix, rows, cols);
|
|||
|
|
dfs(i, j - 1, matrix[i][j], m, matrix, rows, cols);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
/**
|
|||
|
|
* @param {number[][]} matrix
|
|||
|
|
* @return {number[][]}
|
|||
|
|
*/
|
|||
|
|
var pacificAtlantic = function(matrix) {
|
|||
|
|
const rows = matrix.length;
|
|||
|
|
if (rows === 0) return [];
|
|||
|
|
const cols = matrix[0].length;
|
|||
|
|
const pacific = Array.from({
|
|||
|
|
length: rows
|
|||
|
|
},
|
|||
|
|
() = >Array(cols).fill(false));
|
|||
|
|
const atlantic = Array.from({
|
|||
|
|
length: rows
|
|||
|
|
},
|
|||
|
|
() = >Array(cols).fill(false));
|
|||
|
|
const res = [];
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
|
|||
|
|
dfs(i, 0, 0, pacific, matrix, rows, cols);
|
|||
|
|
dfs(i, cols - 1, 0, atlantic, matrix, rows, cols);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
for (let i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
|
|||
|
|
dfs(0, i, 0, pacific, matrix, rows, cols);
|
|||
|
|
dfs(rows - 1, i, 0, atlantic, matrix, rows, cols);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
|
|||
|
|
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
|
|||
|
|
if (pacific[i][j] === true && atlantic[i][j] === true) res.push([i, j]);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
return res;
|
|||
|
|
};
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- C++ Code
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```c++
|
|||
|
|
class Solution {
|
|||
|
|
public:
|
|||
|
|
vector<vector<int> > pacificAtlantic( vector<vector<int> > & matrix )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
vector<vector<int> > out;
|
|||
|
|
int row = matrix.size();
|
|||
|
|
if ( 0 == row )
|
|||
|
|
return(out);
|
|||
|
|
int col = matrix[0].size();
|
|||
|
|
if ( 0 == col )
|
|||
|
|
return(out);
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
/* 能流动到“太平洋"的陆地 */
|
|||
|
|
vector<vector<bool> > dp1( row, vector<bool>( col, false ) );
|
|||
|
|
/* 能流动到“大西洋"的陆地 */
|
|||
|
|
vector<vector<bool> > dp2( row, vector<bool>( col, false ) );
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
/* 从第一行/最后一行出发寻找连同节点,不变的x坐标 */
|
|||
|
|
for ( int j = 0; j < col; j++ )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
dfs( 0, j, INT_MIN, matrix, dp1 );
|
|||
|
|
dfs( row - 1, j, INT_MIN, matrix, dp2 );
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
/* 从第一列/最后一列出发寻找连同节点,不变的y坐标 */
|
|||
|
|
for ( int i = 0; i < row; i++ )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
dfs( i, 0, INT_MIN, matrix, dp1 );
|
|||
|
|
dfs( i, col - 1, INT_MIN, matrix, dp2 );
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
vector<int> temp( 2 );
|
|||
|
|
for ( int i = 0; i < row; i++ )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
for ( int j = 0; j < col; j++ )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
/* 请找出那些水流既可以流动到“太平洋”,又能流动到“大西洋”的陆地单元的坐标。 */
|
|||
|
|
if ( dp1[i][j] == true && dp2[i][j] == true )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
temp[0] = i;
|
|||
|
|
temp[1] = j;
|
|||
|
|
out.push_back( temp );
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
return(out);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
void dfs( int row, int col, int height,
|
|||
|
|
vector<vector<int> > & matrix, vector<vector<bool> > & visited )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
if ( row < 0 || row >= matrix.size() ||
|
|||
|
|
col < 0 || col >= matrix[0].size()
|
|||
|
|
)
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
return;
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
if ( visited[row][col] == true )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
return;
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
if ( height > matrix[row][col] )
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
return;
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
visited[row][col] = true;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
dfs( row + 1, col, matrix[row][col], matrix, visited );
|
|||
|
|
dfs( row - 1, col, matrix[row][col], matrix, visited );
|
|||
|
|
dfs( row, col + 1, matrix[row][col], matrix, visited );
|
|||
|
|
dfs( row, col - 1, matrix[row][col], matrix, visited );
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
};
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
## 其他优秀解答
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
> ##### 暂缺
|