305 lines
6.9 KiB
Markdown
305 lines
6.9 KiB
Markdown
# 题目地址
|
||
|
||
https://leetcode.com/problems/min-stack/description/
|
||
|
||
# 题目描述
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
|
||
|
||
push(x) -- Push element x onto stack.
|
||
pop() -- Removes the element on top of the stack.
|
||
top() -- Get the top element.
|
||
getMin() -- Retrieve the minimum element in the stack.
|
||
Example:
|
||
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
|
||
minStack.push(-2);
|
||
minStack.push(0);
|
||
minStack.push(-3);
|
||
minStack.getMin(); --> Returns -3.
|
||
minStack.pop();
|
||
minStack.top(); --> Returns 0.
|
||
minStack.getMin(); --> Returns -2.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
# 差值法
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
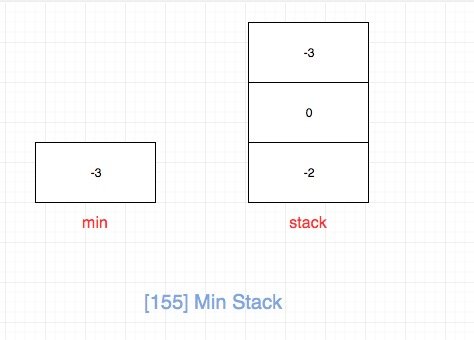
符合直觉的方法是,每次对栈进行修改操作(push和pop)的时候更新最小值。 然后getMin只需要返回我们计算的最小值即可,
|
||
top也是直接返回栈顶元素即可。 这种做法每次修改栈都需要更新最小值,因此时间复杂度是O(n).
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
是否有更高效的算法呢?答案是有的。
|
||
|
||
我们每次入栈的时候,保存的不再是真正的数字,而是它与当前最小值的差(当前元素没有入栈的时候的最小值)。
|
||
这样我们pop和top的时候拿到栈顶元素再加上**上一个**最小值即可。
|
||
另外我们在push和pop的时候去更新min,这样getMin的时候就简单了,直接返回min。
|
||
|
||
> 注意上面加粗的“上一个”,不是“当前的最小值”
|
||
|
||
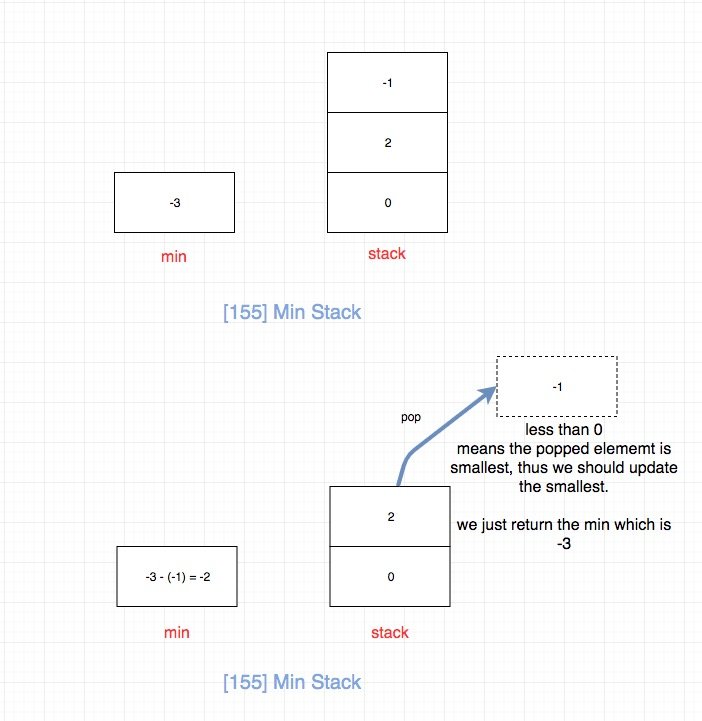
经过上面的分析,问题的关键转化为“如何求得上一个最小值”,解决这个的关键点在于利用min。
|
||
|
||
pop或者top的时候:
|
||
|
||
- 如果栈顶元素小于0,说明栈顶是当前最小的元素,它出栈会对min造成影响,我们需要去更新min。
|
||
上一个最小的是“min - 栈顶元素”,我们需要将上一个最小值更新为当前的最小值
|
||
|
||
> 因为栈顶元素入栈的时候的通过 `栈顶元素 = 真实值 - 上一个最小的元素` 得到的,
|
||
而真实值 = min, 因此可以得出`上一个最小的元素 = 真实值 -栈顶元素`
|
||
|
||
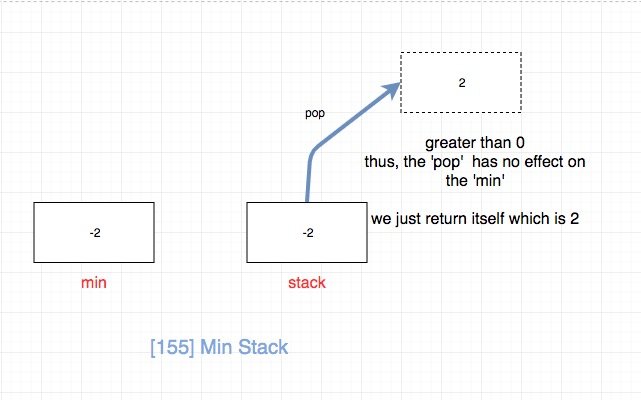
- 如果栈顶元素大于0,说明它对最小值`没有影响`,上一个最小值就是上上个最小值。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 关键点
|
||
|
||
- 最小栈存储的不应该是真实值,而是真实值和min的差值
|
||
- top的时候涉及到对数据的还原,这里千万注意是**上一个**最小值
|
||
|
||
## 代码
|
||
|
||
* 语言支持:JS,Python
|
||
|
||
Javascript Code:
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
/*
|
||
* @lc app=leetcode id=155 lang=javascript
|
||
*
|
||
* [155] Min Stack
|
||
*/
|
||
/**
|
||
* initialize your data structure here.
|
||
*/
|
||
var MinStack = function() {
|
||
this.stack = [];
|
||
this.minV = Number.MAX_VALUE;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @param {number} x
|
||
* @return {void}
|
||
*/
|
||
MinStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
|
||
// update 'min'
|
||
const minV = this.minV;
|
||
if (x < this.minV) {
|
||
this.minV = x;
|
||
}
|
||
return this.stack.push(x - minV);
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @return {void}
|
||
*/
|
||
MinStack.prototype.pop = function() {
|
||
const item = this.stack.pop();
|
||
const minV = this.minV;
|
||
|
||
if (item < 0) {
|
||
this.minV = minV - item;
|
||
return minV;
|
||
}
|
||
return item + minV;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @return {number}
|
||
*/
|
||
MinStack.prototype.top = function() {
|
||
const item = this.stack[this.stack.length - 1];
|
||
const minV = this.minV;
|
||
|
||
if (item < 0) {
|
||
return minV;
|
||
}
|
||
return item + minV;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @return {number}
|
||
*/
|
||
MinStack.prototype.min = function() {
|
||
return this.minV;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
|
||
* var obj = new MinStack()
|
||
* obj.push(x)
|
||
* obj.pop()
|
||
* var param_3 = obj.top()
|
||
* var param_4 = obj.min()
|
||
*/
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Python Code:
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
class MinStack:
|
||
|
||
def __init__(self):
|
||
"""
|
||
initialize your data structure here.
|
||
"""
|
||
self.minV = float('inf')
|
||
self.stack = []
|
||
|
||
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
|
||
self.stack.append(x - self.minV)
|
||
if x < self.minV:
|
||
self.minV = x
|
||
|
||
def pop(self) -> None:
|
||
if not self.stack:
|
||
return
|
||
tmp = self.stack.pop()
|
||
if tmp < 0:
|
||
self.minV -= tmp
|
||
|
||
def top(self) -> int:
|
||
if not self.stack:
|
||
return
|
||
tmp = self.stack[-1]
|
||
if tmp < 0:
|
||
return self.minV
|
||
else:
|
||
return self.minV + tmp
|
||
|
||
def min(self) -> int:
|
||
return self.minV
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
|
||
# obj = MinStack()
|
||
# obj.push(x)
|
||
# obj.pop()
|
||
# param_3 = obj.top()
|
||
# param_4 = obj.min()
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**复杂度分析**
|
||
- 时间复杂度:O(1)
|
||
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 两个栈
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
我们使用两个栈:
|
||
|
||
- 一个栈存放全部的元素,push,pop都是正常操作这个正常栈。
|
||
- 另一个存放最小栈。 每次push,如果比最小栈的栈顶还小,我们就push进最小栈,否则不操作
|
||
- 每次pop的时候,我们都判断其是否和最小栈栈顶元素相同,如果相同,那么我们pop掉最小栈的栈顶元素即可
|
||
|
||
## 关键点
|
||
|
||
- 往minstack中 push的判断条件。 应该是stack为空或者x小于等于minstack栈顶元素
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 代码
|
||
|
||
JavaScript:
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
/**
|
||
* initialize your data structure here.
|
||
*/
|
||
var MinStack = function() {
|
||
this.stack = []
|
||
this.minStack = []
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @param {number} x
|
||
* @return {void}
|
||
*/
|
||
MinStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
|
||
this.stack.push(x)
|
||
if (this.minStack.length == 0 || x <= this.minStack[this.minStack.length - 1]) {
|
||
this.minStack.push(x)
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @return {void}
|
||
*/
|
||
MinStack.prototype.pop = function() {
|
||
const x = this.stack.pop()
|
||
if (x !== void 0 && x === this.minStack[this.minStack.length - 1]) {
|
||
this.minStack.pop()
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @return {number}
|
||
*/
|
||
MinStack.prototype.top = function() {
|
||
return this.stack[this.stack.length - 1]
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @return {number}
|
||
*/
|
||
MinStack.prototype.min = function() {
|
||
return this.minStack[this.minStack.length - 1]
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
|
||
* var obj = new MinStack()
|
||
* obj.push(x)
|
||
* obj.pop()
|
||
* var param_3 = obj.top()
|
||
* var param_4 = obj.min()
|
||
*/
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
Python3:
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
class MinStack:
|
||
|
||
def __init__(self):
|
||
"""
|
||
initialize your data structure here.
|
||
"""
|
||
self.stack = []
|
||
self.minstack = []
|
||
|
||
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
|
||
self.stack.append(x)
|
||
if not self.minstack or x <= self.minstack[-1]:
|
||
self.minstack.append(x)
|
||
|
||
def pop(self) -> None:
|
||
tmp = self.stack.pop()
|
||
if tmp == self.minstack[-1]:
|
||
self.minstack.pop()
|
||
|
||
def top(self) -> int:
|
||
return self.stack[-1]
|
||
|
||
def min(self) -> int:
|
||
return self.minstack[-1]
|
||
|
||
|
||
# Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
|
||
# obj = MinStack()
|
||
# obj.push(x)
|
||
# obj.pop()
|
||
# param_3 = obj.top()
|
||
# param_4 = obj.min()
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**复杂度分析**
|
||
- 时间复杂度:O(1)
|
||
- 空间复杂度:O(N)
|