7.7 KiB
题目地址
https://leetcode.com/problems/median-of-two-sorted-arrays/
题目描述
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively.
Find the median of the two sorted arrays. The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
You may assume nums1 and nums2 cannot be both empty.
Example 1:
nums1 = [1, 3]
nums2 = [2]
The median is 2.0
Example 2:
nums1 = [1, 2]
nums2 = [3, 4]
The median is (2 + 3)/2 = 2.5
思路
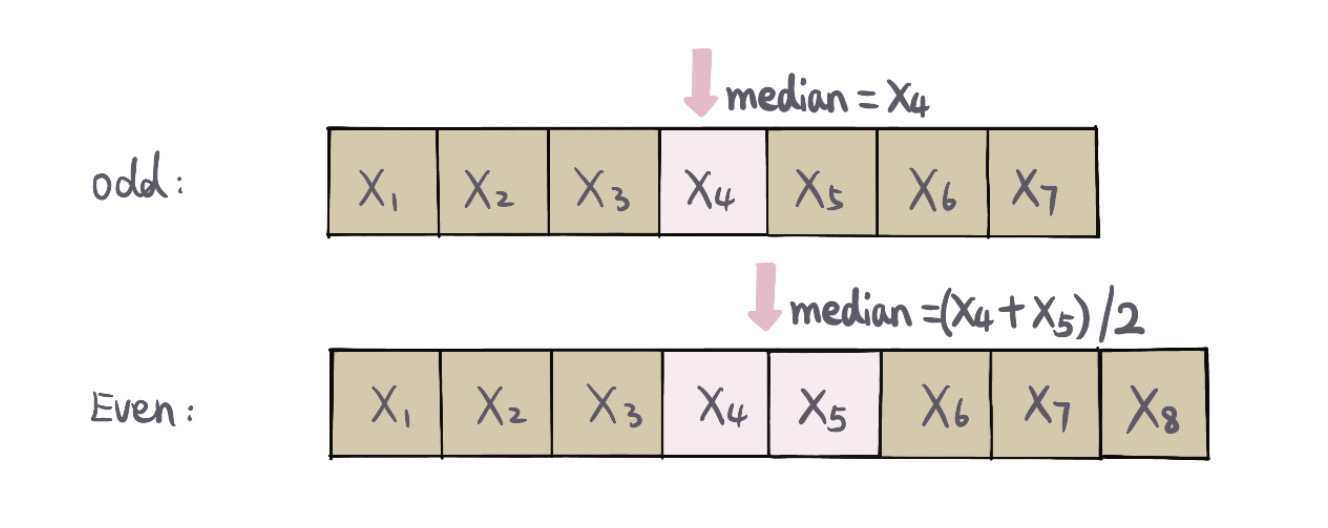
首先了解一下Median的概念,一个数组中median就是把数组分成左右等分的中位数。
这道题,很容易想到暴力解法,时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是O(m+n), 不符合题中给出O(log(m+n))时间复杂度的要求。
我们可以从简单的解法入手,试了一下,暴力解法也是可以被Leetcode Accept的. 分析中会给出两种解法,暴力求解和二分解法。
解法一 - 暴力 (Brute Force)
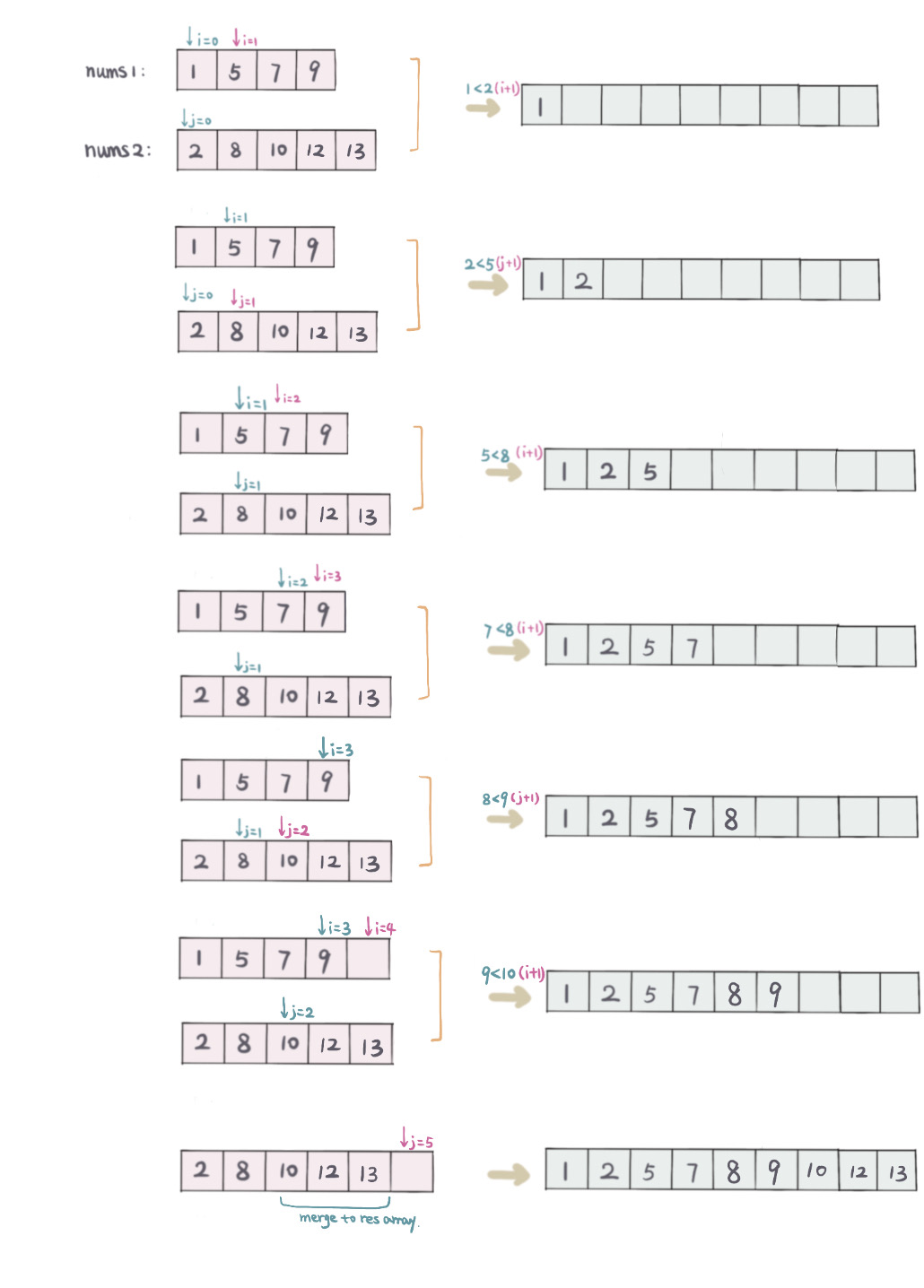
暴力解主要是要merge两个排序的数组(A,B)成一个排序的数组。
用两个pointer(i,j),i 从数组A起始位置开始,即i=0开始,j 从数组B起始位置, 即j=0开始.
一一比较 A[i] 和 B[j],
- 如果
A[i] <= B[j], 则把A[i]放入新的数组中,i往后移一位,即i+1. - 如果
A[i] > B[j], 则把B[j]放入新的数组中,j往后移一位,即j+1. - 重复步骤#1 和 #2,直到
i移到A最后,或者j移到B最后。 - 如果
j移动到B数组最后,那么直接把剩下的所有A依次放入新的数组中. - 如果
i移动到A数组最后,那么直接把剩下的所有B依次放入新的数组中.
时间复杂度: O(m+n) - m is length of A, n is length of B
空间复杂度: O(m+n)
解法二 - 二分查找 (Binary Search)
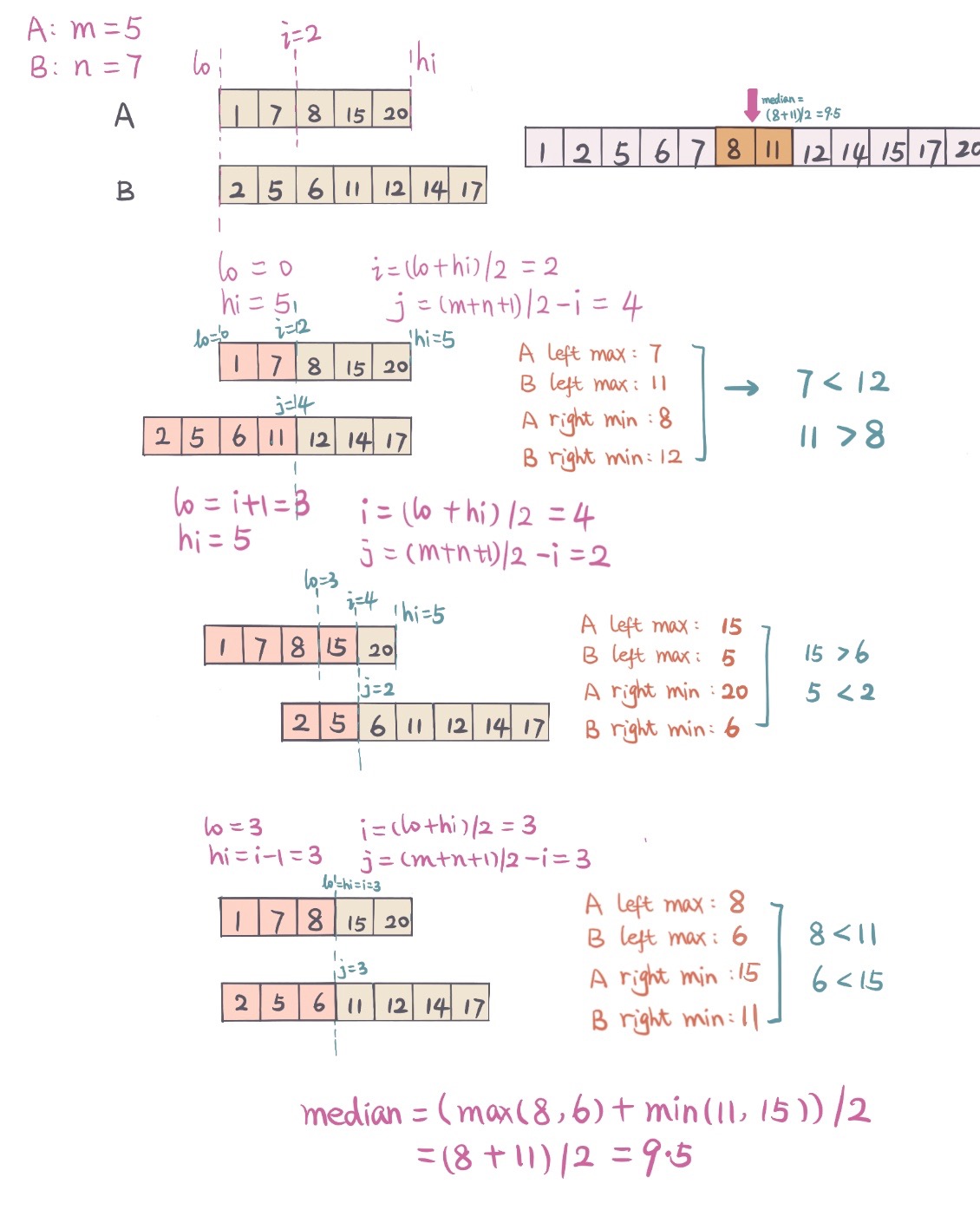
由于题中给出的数组都是排好序的,在排好序的数组中查找很容易想到可以用二分查找(Binary Search), 这里对数组长度小的做二分, 保证数组A 和 数组B 做partition 之后
len(Aleft)+len(Bleft)=(m+n+1)/2 - m是数组A的长度, n是数组B的长度
对数组A的做partition的位置是区间[0,m]
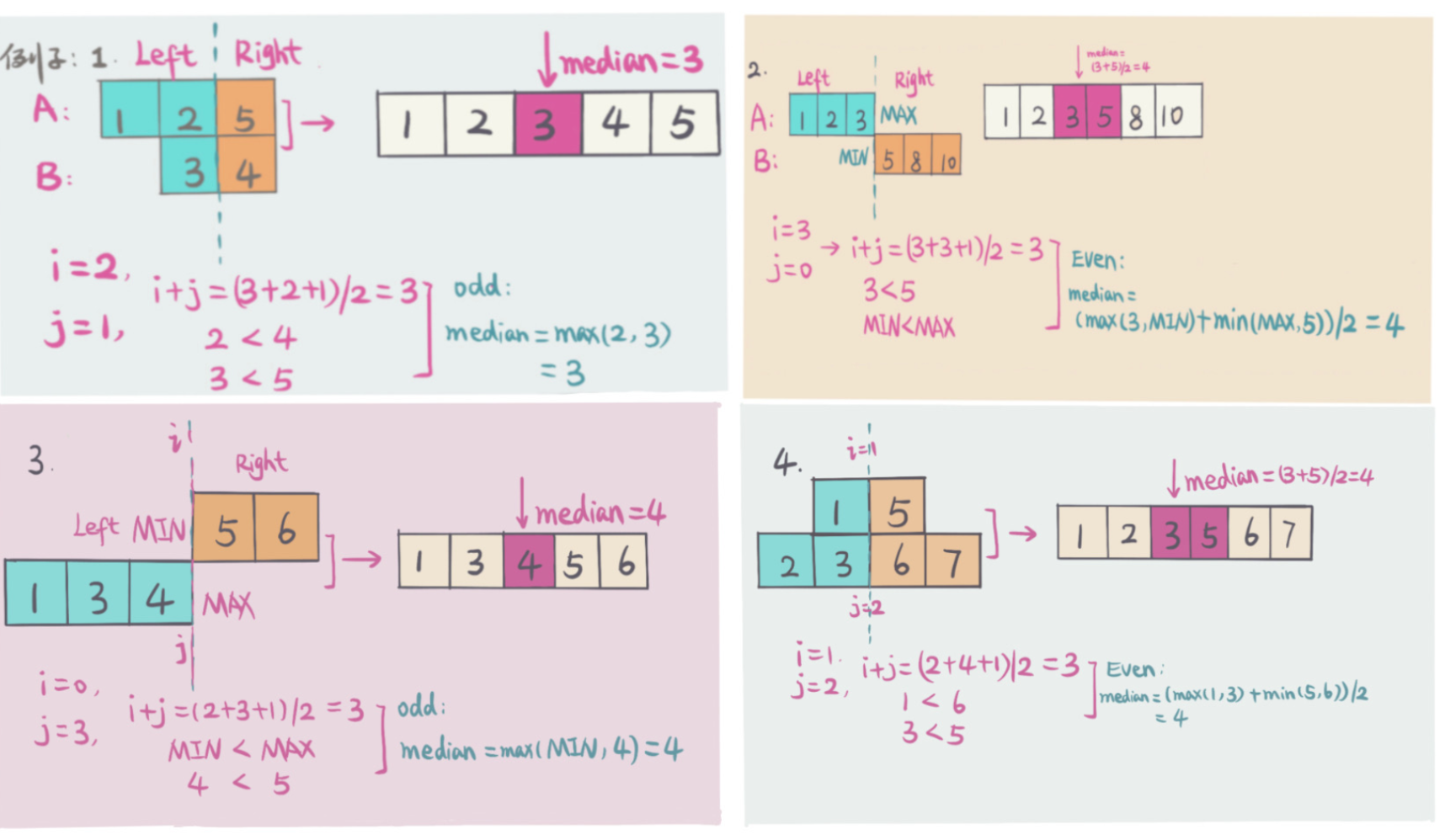
下图给出几种不同情况的例子(注意但左边或者右边没有元素的时候,左边用INF_MIN,右边用INF_MAX表示左右的元素:
时间复杂度: O(log(min(m, n)) - m is length of A, n is length of B
空间复杂度: O(1) - 这里没有用额外的空间
关键点分析
- 暴力求解,在线性时间内merge两个排好序的数组成一个数组。
- 二分查找,关键点在于
-
要partition两个排好序的数组成左右两等份,partition需要满足
len(Aleft)+len(Bleft)=(m+n+1)/2 - m是数组A的长度, n是数组B的长度 -
并且partition后 A左边最大(
maxLeftA), A右边最小(minRightA), B左边最大(maxLeftB), B右边最小(minRightB) 满足(maxLeftA <= minRightB && maxLeftB <= minRightA)
有了这两个条件,那么median就在这四个数中,根据奇数或者是偶数,
奇数:
median = max(maxLeftA, maxLeftB)
偶数:
median = (max(maxLeftA, maxLeftB) + min(minRightA, minRightB)) / 2
代码(Java code)
解法一 - 暴力解法(Brute force)
class MedianTwoSortedArrayBruteForce {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int[] newArr = mergeTwoSortedArray(nums1, nums2);
int n = newArr.length;
if (n % 2 == 0) {
// even
return (double) (newArr[n / 2] + newArr[n / 2 - 1]) / 2;
} else {
// odd
return (double) newArr[n / 2];
}
}
private int[] mergeTwoSortedArray(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int m = nums1.length;
int n = nums2.length;
int[] res = new int[m + n];
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int idx = 0;
while (i < m && j < n) {
if (nums1[i] <= nums2[j]) {
res[idx++] = nums1[i++];
} else {
res[idx++] = nums2[j++];
}
}
while (i < m) {
res[idx++] = nums1[i++];
}
while (j < n) {
res[idx++] = nums2[j++];
}
return res;
}
}
解法二 - 二分查找(Binary Search)
class MedianSortedTwoArrayBinarySearch {
public static double findMedianSortedArraysBinarySearch(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
// do binary search for shorter length array, make sure time complexity log(min(m,n)).
if (nums1.length > nums2.length) {
return findMedianSortedArraysBinarySearch(nums2, nums1);
}
int m = nums1.length;
int n = nums2.length;
int lo = 0;
int hi = m;
while (lo <= hi) {
// partition A position i
int i = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
// partition B position j
int j = (m + n + 1) / 2 - i;
int maxLeftA = i == 0 ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : nums1[i - 1];
int minRightA = i == m ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : nums1[i];
int maxLeftB = j == 0 ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : nums2[j - 1];
int minRightB = j == n ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : nums2[j];
if (maxLeftA <= minRightB && maxLeftB <= minRightA) {
// total length is even
if ((m + n) % 2 == 0) {
return (double) (Math.max(maxLeftA, maxLeftB) + Math.min(minRightA, minRightB)) / 2;
} else {
// total length is odd
return (double) Math.max(maxLeftA, maxLeftB);
}
} else if (maxLeftA > minRightB) {
// binary search left half
hi = i - 1;
} else {
// binary search right half
lo = i + 1;
}
}
return 0.0;
}
}
代码 (javascript code)
解法一 - 暴力解法(Brute force)
/**
* @param {number[]} nums1
* @param {number[]} nums2
* @return {number}
*/
var findMedianSortedArrays = function(nums1, nums2) {
// 归并排序
const merged = []
let i = 0
let j = 0
while(i < nums1.length && j < nums2.length) {
if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {
merged.push(nums1[i++])
} else {
merged.push(nums2[j++])
}
}
while(i < nums1.length) {
merged.push(nums1[i++])
}
while(j < nums2.length) {
merged.push(nums2[j++])
}
const { length } = merged
return length % 2 === 1
? merged[Math.floor(length / 2)]
: (merged[length / 2] + merged[length / 2 - 1]) / 2
};
解法二 - 二分查找(Binary Search)
/**
* 二分解法
* @param {number[]} nums1
* @param {number[]} nums2
* @return {number}
*/
var findMedianSortedArrays = function(nums1, nums2) {
// make sure to do binary search for shorten array
if (nums1.length > nums2.length) {
[nums1, nums2] = [nums2, nums1]
}
const m = nums1.length
const n = nums2.length
let low = 0
let high = m
while(low <= high) {
const i = low + Math.floor((high - low) / 2)
const j = Math.floor((m + n + 1) / 2) - i
const maxLeftA = i === 0 ? -Infinity : nums1[i-1]
const minRightA = i === m ? Infinity : nums1[i]
const maxLeftB = j === 0 ? -Infinity : nums2[j-1]
const minRightB = j === n ? Infinity : nums2[j]
if (maxLeftA <= minRightB && minRightA >= maxLeftB) {
return (m + n) % 2 === 1
? Math.max(maxLeftA, maxLeftB)
: (Math.max(maxLeftA, maxLeftB) + Math.min(minRightA, minRightB)) / 2
} else if (maxLeftA > minRightB) {
high = i - 1
} else {
low = low + 1
}
}
};