diff --git a/machine_learning/adaline_learning.cpp b/machine_learning/adaline_learning.cpp
index 1e25d3ba1..a8426ac4e 100644
--- a/machine_learning/adaline_learning.cpp
+++ b/machine_learning/adaline_learning.cpp
@@ -7,10 +7,12 @@
*
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
*
- * ![]()
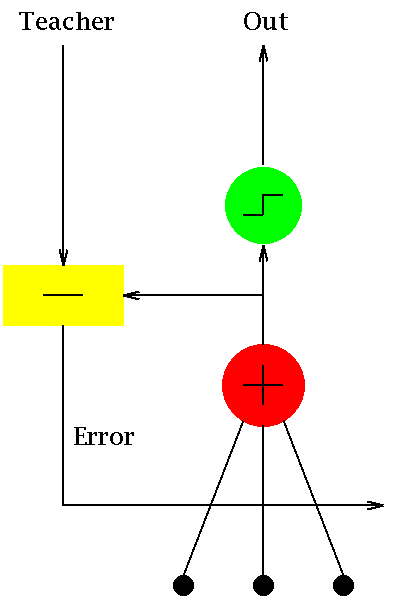 - * [source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adaline_flow_chart.gif)
+ * alt="Structure of an ADALINE network. Source: Wikipedia"
+ * style="width:200px; float:right;">
+ *
* ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural
* network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
* \f[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) =
diff --git a/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp b/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
index 25c58e260..016fe6d1e 100644
--- a/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
+++ b/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
@@ -3,9 +3,11 @@
* @{
* \file
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
+ *
* \brief [Kohonen self organizing
* map](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-organizing_map) (topological map)
*
+ * \details
* This example implements a powerful unsupervised learning algorithm called as
* a self organizing map. The algorithm creates a connected network of weights
* that closely follows the given data points. This thus creates a topological
@@ -21,7 +23,7 @@
* than with GCC on windows
* \see kohonen_som_trace.cpp
*/
-#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES // required for MS Visual C++
+#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES //< required for MS Visual C++
#include
#include
#include
diff --git a/numerical_methods/newton_raphson_method.cpp b/numerical_methods/newton_raphson_method.cpp
index d086123ca..7597f1b8a 100644
--- a/numerical_methods/newton_raphson_method.cpp
+++ b/numerical_methods/newton_raphson_method.cpp
@@ -17,17 +17,24 @@
#include
#include
-#define EPSILON \
- 1e-6 // std::numeric_limits::epsilon() ///< system accuracy limit
-#define MAX_ITERATIONS 50000 ///< Maximum number of iterations to check
+#define EPSILON 1e-10 ///< system accuracy limit
+#define MAX_ITERATIONS INT16_MAX ///< Maximum number of iterations to check
-/** define \f$f(x)\f$ to find root for
+/** define \f$f(x)\f$ to find root for.
+ * Currently defined as:
+ * \f[
+ * f(x) = x^3 - 4x - 9
+ * \f]
*/
static double eq(double i) {
return (std::pow(i, 3) - (4 * i) - 9); // original equation
}
/** define the derivative function \f$f'(x)\f$
+ * For the current problem, it is:
+ * \f[
+ * f'(x) = 3x^2 - 4
+ * \f]
*/
static double eq_der(double i) {
return ((3 * std::pow(i, 2)) - 4); // derivative of equation
diff --git a/numerical_methods/ordinary_least_squares_regressor.cpp b/numerical_methods/ordinary_least_squares_regressor.cpp
index 43979d0ea..bbd75a742 100644
--- a/numerical_methods/ordinary_least_squares_regressor.cpp
+++ b/numerical_methods/ordinary_least_squares_regressor.cpp
@@ -3,10 +3,11 @@
* \brief Linear regression example using [Ordinary least
* squares](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ordinary_least_squares)
*
- * \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
* Program that gets the number of data samples and number of features per
* sample along with output per sample. It applies OLS regression to compute
* the regression output for additional test data samples.
+ *
+ * \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
*/
#include // for print formatting
#include
- * [source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adaline_flow_chart.gif)
+ * alt="Structure of an ADALINE network. Source: Wikipedia"
+ * style="width:200px; float:right;">
+ *
* ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural
* network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
* \f[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) =
diff --git a/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp b/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
index 25c58e260..016fe6d1e 100644
--- a/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
+++ b/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
@@ -3,9 +3,11 @@
* @{
* \file
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
+ *
* \brief [Kohonen self organizing
* map](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-organizing_map) (topological map)
*
+ * \details
* This example implements a powerful unsupervised learning algorithm called as
* a self organizing map. The algorithm creates a connected network of weights
* that closely follows the given data points. This thus creates a topological
@@ -21,7 +23,7 @@
* than with GCC on windows
* \see kohonen_som_trace.cpp
*/
-#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES // required for MS Visual C++
+#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES //< required for MS Visual C++
#include
#include
#include
diff --git a/numerical_methods/newton_raphson_method.cpp b/numerical_methods/newton_raphson_method.cpp
index d086123ca..7597f1b8a 100644
--- a/numerical_methods/newton_raphson_method.cpp
+++ b/numerical_methods/newton_raphson_method.cpp
@@ -17,17 +17,24 @@
#include
#include
-#define EPSILON \
- 1e-6 // std::numeric_limits::epsilon() ///< system accuracy limit
-#define MAX_ITERATIONS 50000 ///< Maximum number of iterations to check
+#define EPSILON 1e-10 ///< system accuracy limit
+#define MAX_ITERATIONS INT16_MAX ///< Maximum number of iterations to check
-/** define \f$f(x)\f$ to find root for
+/** define \f$f(x)\f$ to find root for.
+ * Currently defined as:
+ * \f[
+ * f(x) = x^3 - 4x - 9
+ * \f]
*/
static double eq(double i) {
return (std::pow(i, 3) - (4 * i) - 9); // original equation
}
/** define the derivative function \f$f'(x)\f$
+ * For the current problem, it is:
+ * \f[
+ * f'(x) = 3x^2 - 4
+ * \f]
*/
static double eq_der(double i) {
return ((3 * std::pow(i, 2)) - 4); // derivative of equation
diff --git a/numerical_methods/ordinary_least_squares_regressor.cpp b/numerical_methods/ordinary_least_squares_regressor.cpp
index 43979d0ea..bbd75a742 100644
--- a/numerical_methods/ordinary_least_squares_regressor.cpp
+++ b/numerical_methods/ordinary_least_squares_regressor.cpp
@@ -3,10 +3,11 @@
* \brief Linear regression example using [Ordinary least
* squares](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ordinary_least_squares)
*
- * \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
* Program that gets the number of data samples and number of features per
* sample along with output per sample. It applies OLS regression to compute
* the regression output for additional test data samples.
+ *
+ * \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
*/
#include // for print formatting
#include
 - * [source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adaline_flow_chart.gif)
+ * alt="Structure of an ADALINE network. Source: Wikipedia"
+ * style="width:200px; float:right;">
+ *
* ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural
* network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
* \f[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) =
diff --git a/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp b/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
index 25c58e260..016fe6d1e 100644
--- a/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
+++ b/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
@@ -3,9 +3,11 @@
* @{
* \file
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
+ *
* \brief [Kohonen self organizing
* map](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-organizing_map) (topological map)
*
+ * \details
* This example implements a powerful unsupervised learning algorithm called as
* a self organizing map. The algorithm creates a connected network of weights
* that closely follows the given data points. This thus creates a topological
@@ -21,7 +23,7 @@
* than with GCC on windows
* \see kohonen_som_trace.cpp
*/
-#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES // required for MS Visual C++
+#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES //< required for MS Visual C++
#include
- * [source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adaline_flow_chart.gif)
+ * alt="Structure of an ADALINE network. Source: Wikipedia"
+ * style="width:200px; float:right;">
+ *
* ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural
* network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
* \f[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) =
diff --git a/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp b/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
index 25c58e260..016fe6d1e 100644
--- a/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
+++ b/machine_learning/kohonen_som_topology.cpp
@@ -3,9 +3,11 @@
* @{
* \file
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
+ *
* \brief [Kohonen self organizing
* map](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-organizing_map) (topological map)
*
+ * \details
* This example implements a powerful unsupervised learning algorithm called as
* a self organizing map. The algorithm creates a connected network of weights
* that closely follows the given data points. This thus creates a topological
@@ -21,7 +23,7 @@
* than with GCC on windows
* \see kohonen_som_trace.cpp
*/
-#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES // required for MS Visual C++
+#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES //< required for MS Visual C++
#include