Adaptive Linear Neuron (ADALINE) implementation More...
#include <assert.h>#include <limits.h>#include <math.h>#include <stdbool.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>Data Structures | |
| struct | adaline |
| structure to hold adaline model parameters More... | |
Macros | |
| #define | MAX_ITER 500 |
| Maximum number of iterations to learn. | |
| #define | ACCURACY 1e-5 |
| convergence accuracy \(=1\times10^{-5}\) | |
Functions | |
| struct adaline | new_adaline (const int num_features, const double eta) |
| Default constructor. More... | |
| void | delete_adaline (struct adaline *ada) |
| delete dynamically allocated memory More... | |
| int | activation (double x) |
| Heaviside activation function | |
| char * | get_weights_str (struct adaline *ada) |
| Operator to print the weights of the model. | |
| int | predict (struct adaline *ada, const double *x, double *out) |
| predict the output of the model for given set of features More... | |
| double | fit_sample (struct adaline *ada, const double *x, const int y) |
| Update the weights of the model using supervised learning for one feature vector. More... | |
| void | fit (struct adaline *ada, double **X, const int *y, const int N) |
| Update the weights of the model using supervised learning for an array of vectors. More... | |
| void | test1 (double eta) |
| test function to predict points in a 2D coordinate system above the line \(x=y\) as +1 and others as -1. More... | |
| void | test2 (double eta) |
| test function to predict points in a 2D coordinate system above the line \(x+3y=-1\) as +1 and others as -1. More... | |
| void | test3 (double eta) |
| test function to predict points in a 3D coordinate system lying within the sphere of radius 1 and centre at origin as +1 and others as -1. More... | |
| int | main (int argc, char **argv) |
| Main function. | |
Detailed Description
Adaptive Linear Neuron (ADALINE) implementation
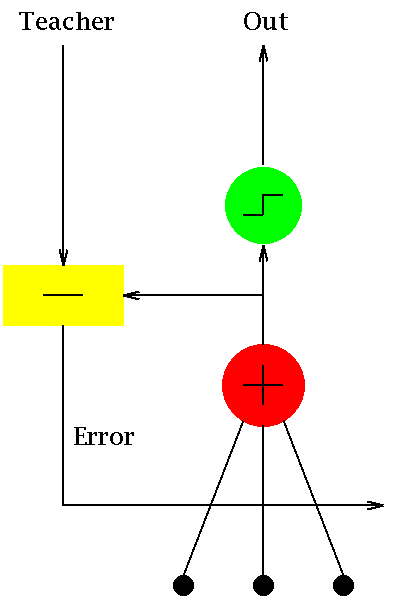 source ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
source ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
\[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) = \sum_j x_jw_j+\theta \]
where \(x_j\) are the input features of a sample, \(w_j\) are the coefficients of the linear function and \(\theta\) is a constant. If we know the \(w_j\), then for any given set of features, \(y\) can be computed. Computing the \(w_j\) is a supervised learning algorithm wherein a set of features and their corresponding outputs are given and weights are computed using stochastic gradient descent method.
Function Documentation
◆ delete_adaline()
| void delete_adaline | ( | struct adaline * | ada | ) |
delete dynamically allocated memory
- Parameters
-
[in] ada model from which the memory is to be freeed.
◆ fit()
| void fit | ( | struct adaline * | ada, |
| double ** | X, | ||
| const int * | y, | ||
| const int | N | ||
| ) |
Update the weights of the model using supervised learning for an array of vectors.
- Parameters
-
[in] ada adaline model to train [in] X array of feature vector [in] y known output value for each feature vector [in] N number of training samples
◆ fit_sample()
| double fit_sample | ( | struct adaline * | ada, |
| const double * | x, | ||
| const int | y | ||
| ) |
Update the weights of the model using supervised learning for one feature vector.
- Parameters
-
[in] ada adaline model to fit [in] x feature vector [in] y known output value
- Returns
- correction factor
◆ new_adaline()
| struct adaline new_adaline | ( | const int | num_features, |
| const double | eta | ||
| ) |
Default constructor.
- Parameters
-
[in] num_features number of features present [in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.1)
- Returns
- new adaline model
◆ predict()
| int predict | ( | struct adaline * | ada, |
| const double * | x, | ||
| double * | out | ||
| ) |
predict the output of the model for given set of features
- Parameters
-
[in] ada adaline model to predict [in] x input vector [out] out optional argument to return neuron output before applying activation function ( NULLto ignore)
- Returns
- model prediction output
◆ test1()
| void test1 | ( | double | eta | ) |
test function to predict points in a 2D coordinate system above the line \(x=y\) as +1 and others as -1.
Note that each point is defined by 2 values or 2 features.
- Parameters
-
[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
◆ test2()
| void test2 | ( | double | eta | ) |
test function to predict points in a 2D coordinate system above the line \(x+3y=-1\) as +1 and others as -1.
Note that each point is defined by 2 values or 2 features. The function will create random sample points for training and test purposes.
- Parameters
-
[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
◆ test3()
| void test3 | ( | double | eta | ) |
test function to predict points in a 3D coordinate system lying within the sphere of radius 1 and centre at origin as +1 and others as -1.
Note that each point is defined by 3 values but we use 6 features. The function will create random sample points for training and test purposes. The sphere centred at origin and radius 1 is defined as: \(x^2+y^2+z^2=r^2=1\) and if the \(r^2<1\), point lies within the sphere else, outside.
- Parameters
-
[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
